Manual
⇒ Search napRNA of genome
- Step1: Users can select a target genome on the homepage by clicking the “Homo sapiens” module or “Mus musculus” module, then choose a napRNA type, and click “Submit” to view information about this type of napRNA in the genome.
- Step2: Click "Browser" to display the detail information about this napRNA. And the details will be displayed in the detail information section that is below the query page.

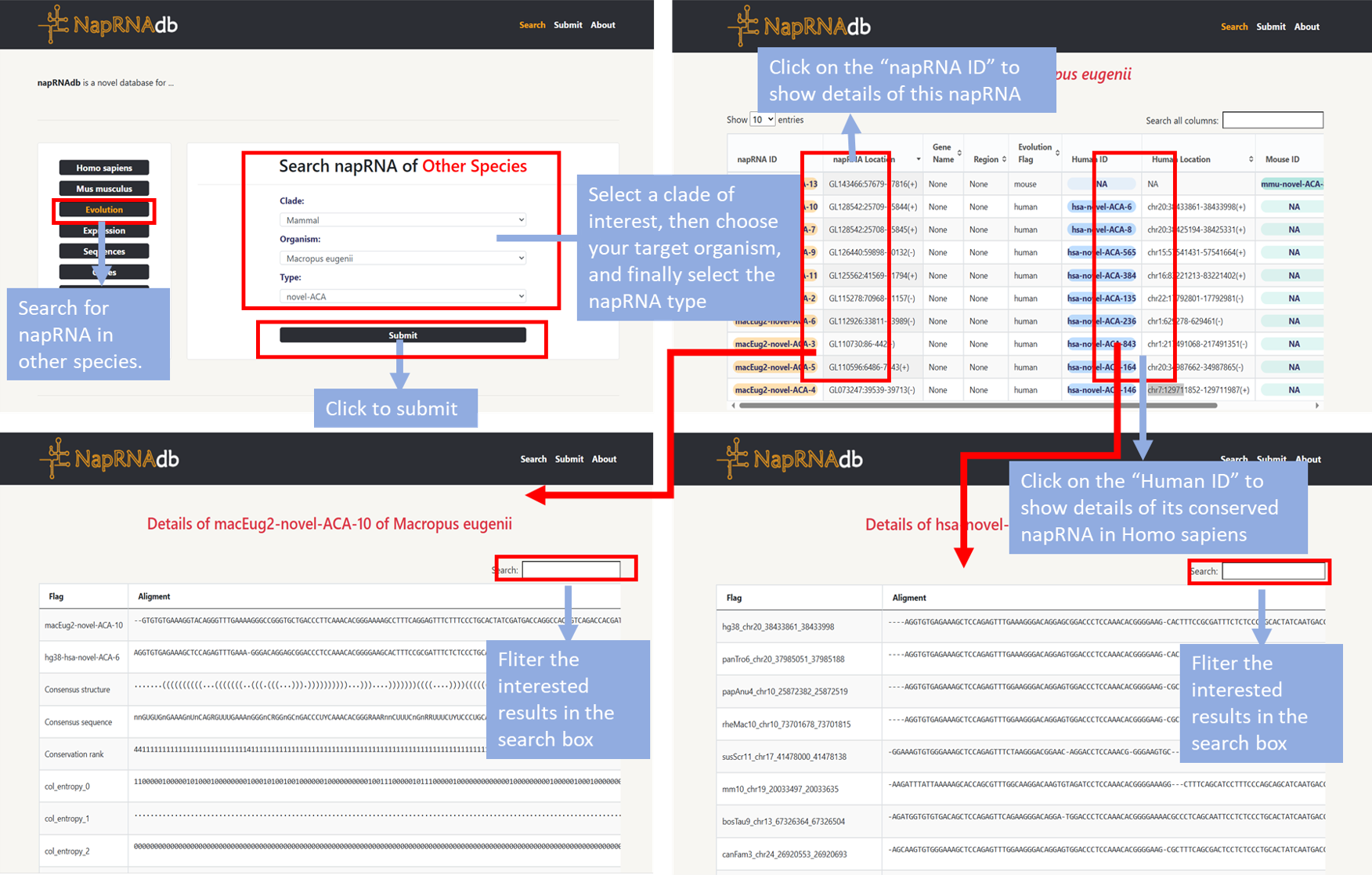
⇒ Evolution
- Step1: Users can click the "Evolution" module on the homepage to search for napRNA in other species.
- Step2: Select a clade of interest, then choose your target organism, and finally select the napRNA type before clicking "Submit". Information about this napRNA in the genome will be displayed on a new page.
- Step3: Click "napRNA ID" to display the detail information about this napRNA. Click "Human ID" or “Mose ID” to jump to the detail page of its conserved napRNA in Homo sapiens or Mus musculus.
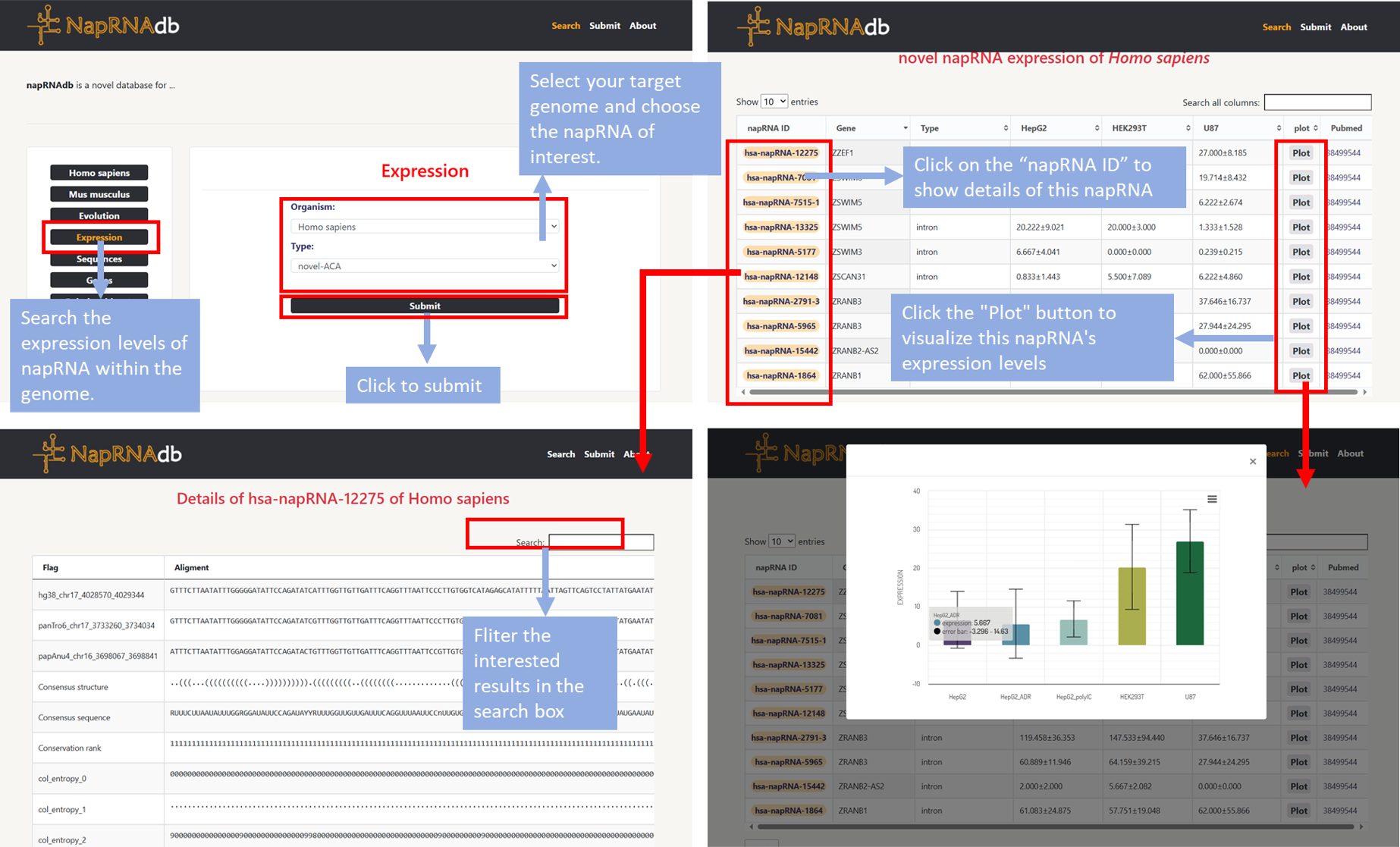
⇒ Expression
- Step1: Users can click the Expression module on the homepage to search the expression levels of napRNA within the genome.
- Step2: In the "organism" section, select your target genome. In the "type" field, choose the napRNA of interest, then click "Submit". The expression levels of this napRNA in the genome will be displayed on a new page.
- Step3: Click "napRNA ID" to display the detail information about this napRNA. Click the "Plot" button to visualize this napRNA's expression levels across different cell types.
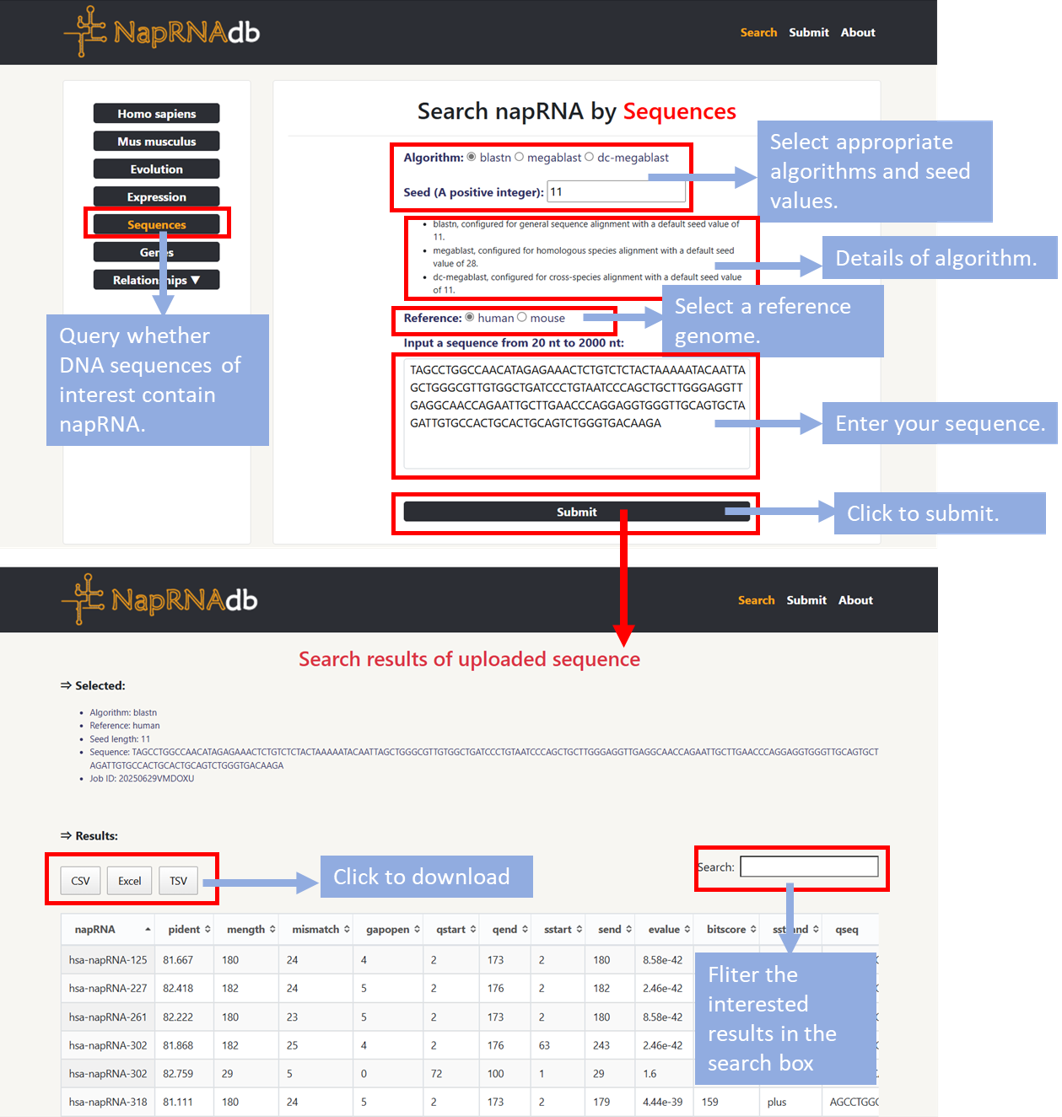
⇒ Predict
- Step1: Users can click the “Sequence” module on the homepage to query whether DNA sequences of interest contain napRNA.
- Step2: Select appropriate algorithms and seed values. Higher seed values yield more precise results, while lower values generate more matches (for details, refer to the blastn algorithm principle).
- Step3: Select a reference genome, enter your sequence, and click “Submit”. BLAST results will be displayed in a new page.
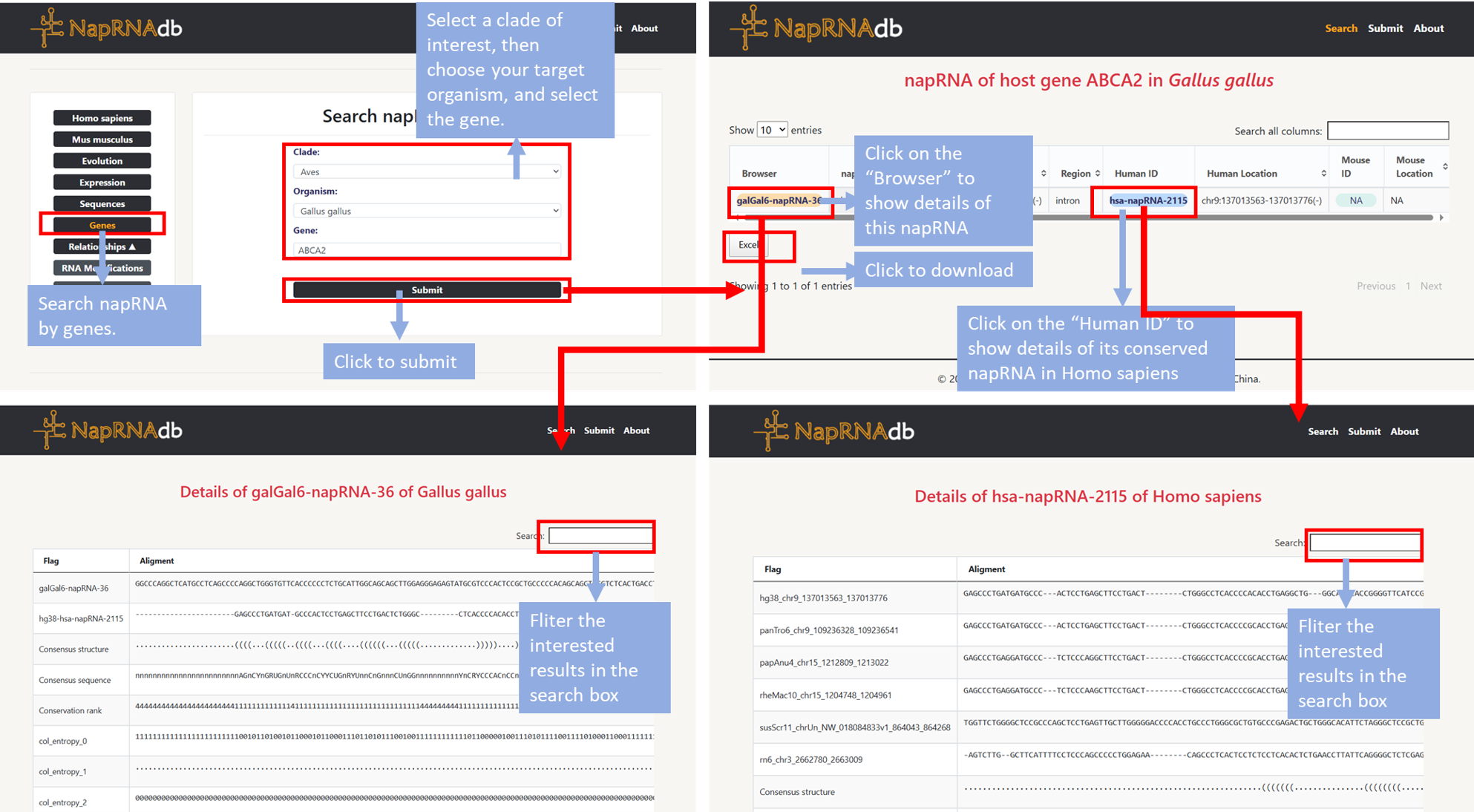
⇒ Gene
- Step1: Users can click the "Gene" module on the homepage to search napRNA by genes.
- Step2: Select a clade of interest, then choose your target organism, and finally select the gene before clicking "Submit". Information about the napRNA of host gene in organsim will be displayed on a new page.
- Step3: Click "Browser" to display the detail information about this napRNA. Click "Human ID" or “Mose ID” to jump to the detail page of its conserved napRNA in Homo sapiens or Mus musculus.
⇒ Relationships
- Step1: Users can explore napRNA's relationships with RNA modifications or RBP-binding events through the RNA Modifications module or RBP-binding Events module.
- Step2: Select your target organism, choose a napRNA type, and finally click "Submit".Click "napRNA ID" to display the detail information about this napRNA.
- Step3: When using the RNA Modifications module, users can click the value of the "modID" column to jump to rmbase to view the details of the RNA modification site. When using the RBP-binding Events module, users can click the value of the "Accession" column to jump the corresponding database to view the details of this RBP.

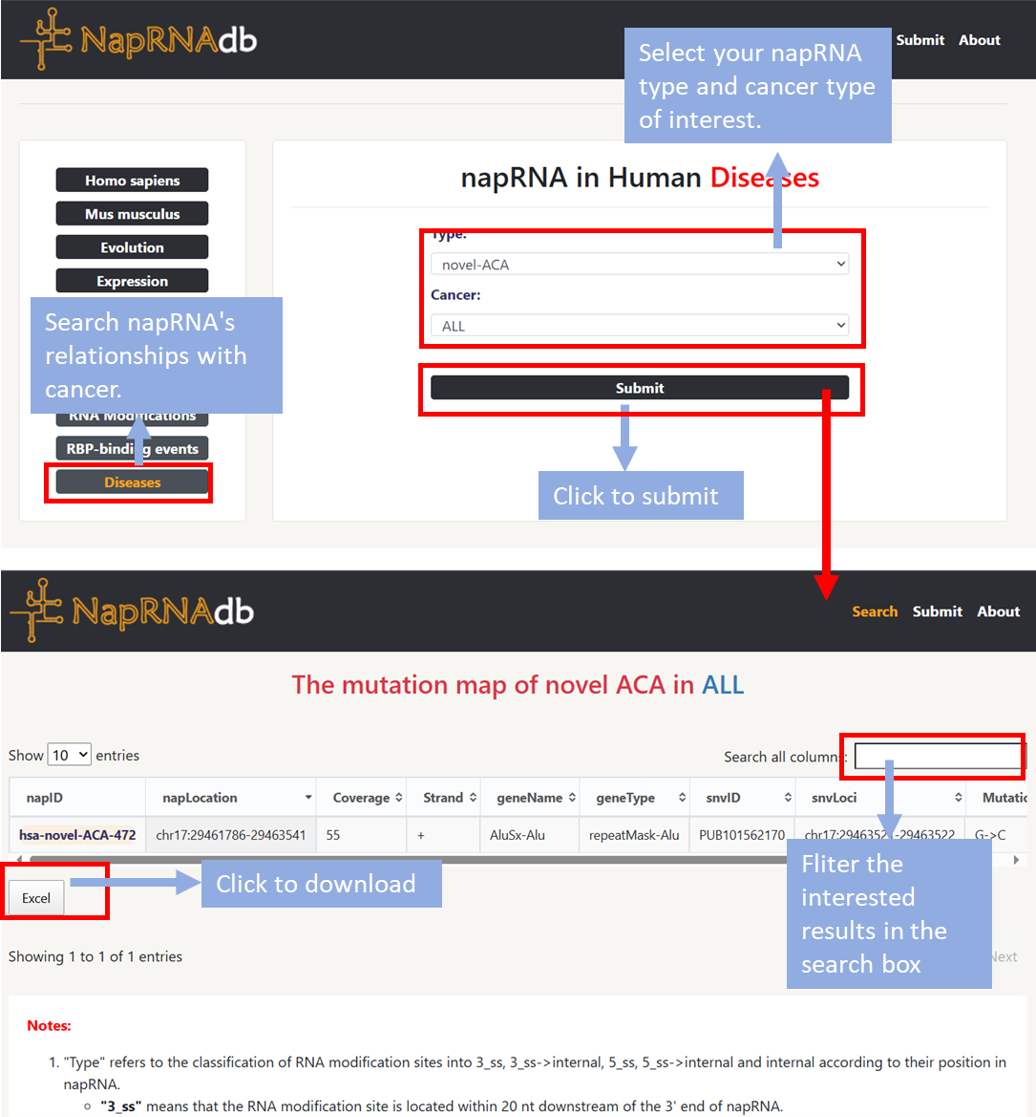
⇒ napRNA in Human Diseases
- Step1: Users can select the Diseases module within Relationships to view mutation information of napRNA across cancer types.
- Step2: Select your napRNA type and cancer type of interest, then click Submit. The mutation map of the napRNA in cancer will be displayed on a new page.
Terminology
- Table 1: Classification and definition of napRNAs
- Table 2: Abbreviations to their full names for diseases
- Table 3: Latin names and common names for species
| Classification | Definition |
|---|---|
| sliRNAs (stable linear intron RNAs) | linear napRNAs that overlap with entire intron regions, contain both 5′ and 3′ splice sites (5′-ss and 3′-ss), and are stably expressed in vivo |
| snotrons (snoRNA-intron napRNAs) | napRNAs whose one end corresponds to the 5’/3’-end position of an intronic snoRNA and the other end corresponds to the 3’/5’-end of an intron |
| misRNAs (napRNAs embedded in miRNA spacer regions) | linear napRNAs that map to the sequences of miRNA spacer regions, with each end coinciding with one end of the two mature miRNAs |
| Pol3-napRNAs | napRNAs, transcribed by RNA polymerase III (pol III) and primarily processed from repetitive elements, that contain A/B box promoters and a 4U stretch at the 3’-end, and can fold into complex stem-loop structures |
| H/ACA napRNAs | H/ACA box snoRNAs identified from NAP-seq profiles, which reside within various known repetitive elements. Notably, H/ACA box napRNAs are significantly longer than their canonical counterparts, representing long napRNAs typically missed by conventional sRNA-seq |
| C/D napRNAs | C/D box snoRNAs identified from NAP-seq profiles, which reside within various known repetitive elements. Notably, C/D box napRNAs are significantly longer than their canonical counterparts, representing long napRNAs typically missed by conventional sRNA-seq |
| polyA-pocket-ACA napRNAs | H/ACA snoRNAs containing a poly(A) pocket |
| Abbreviation | Full name |
|---|---|
| ACC | Adrenocortical Carcinoma |
| ALL | Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia |
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| BLCA | Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma |
| BRCA | Breast Invasive Carcinoma |
| CARC | Carcinoid |
| CESC | Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Endocervical Adenocarcinoma |
| CHOL | Cholangiocarcinoma |
| CLL | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia |
| CRC | Colorectal |
| DLBCL | Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma |
| ESCA | Esophageal Carcinoma |
| ESO | Esophageal Adenocarcinoma |
| FMTC | Familial Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma |
| GBM | Glioblastoma Multiforme |
| HCC | Tepatocellular Carcinom |
| HNSC | Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| KIRC | Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma |
| KIRP | Kidney Renal Papillary Cell Carcinoma |
| LCML | Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia |
| LGG | Brain Lower Grade Glioma |
| LIHC | Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| LUAD | Lung Adenocarcinoma |
| LUSC | Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| MED | Medulloblastoma |
| MEL | Melanoma |
| MM | Multiple Myeloma |
| NB | Neuroblastoma |
| OV | Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma |
| PA | Pilocytic Astrocytoma |
| PET | Pancreatic Endocrine Tumor |
| PRAD | Prostate Adenocarcinoma |
| SARC | Sarcoma |
| SCLC | Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| SKCM | Skin Cutaneous Melanoma |
| STAD | Stomach Adenocarcinoma |
| TGCT | Testicular Germ Cell Tumors |
| THCA | Thyroid Carcinoma |
| UCEC | Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma |
| Latin name | Common name | Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Anolis carolinensis | Lizard | anoCar2 |
| Bos taurus | Cow | bosTau9 |
| Callithrix jacchus | Marmoset | calJac4 |
| Canis lupus familiaris | Dog | canFam3 |
| Cavia porcellus | Guinea_pig | cavPor3 |
| Chlorocebus sabaeus | Green_monkey | chlSab2 |
| Cricetulus griseus | Chinese_hamster | criGriChoV2 |
| Danio rerio | Zebrafish | danRer11 |
| Dipodomys ordii | Kangaroo_rat | dipOrd1 |
| Equus caballus | Horse | equCab3 |
| Felis catus | Cat | felCat9 |
| Gallus gallus | Chicken | galGal6 |
| Gorilla gorilla | Gorilla | gorGor5 |
| Heterocephalus glaber | Naked_mole_rat | hetGla2 |
| Homo sapiens | Human | hg38 |
| Macaca mulatta | Rhesus | rheMac10 |
| Macropus eugenii | Wallaby | macEug2 |
| Microcebus murinus | Mouse_lemur | micMur2 |
| Monodelphis domestica | Opossum | monDom5 |
| Mus musculus | Mouse | mm10 |
| Nomascus leucogenys | Gibbon | nomLeu3 |
| Ochotona princeps | Pika | ochPri3 |
| Ornithorhynchus anatinus | Platypus | ornAna2 |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus | Rabbit | oryCun2 |
| Otolemur garnettii | Bushbaby | otoGar3 |
| Ovis aries | Sheep | oviAri4 |
| Pan troglodytes | Chimp | panTro6 |
| Papio hamadryas | Baboon | papAnu4 |
| Pongo pygmaeus abelii | Orangutan | ponAbe3 |
| Rattus norvegicus | Rat | rn6 |
| Saimiri boliviensis | Squirrel_monkey | saiBol1 |
| Sorex araneus | Shrew | sorAra2 |
| Spermophilus tridecemlineatus | Squirrel | speTri2 |
| Sus scrofa | Pig | susScr11 |
| Takifugu rubripes | Fugu | fr3 |
| Tarsius syrichta | Tarsier | tarSyr2 |
| Trichechus manatus latirostris | Manatee | triMan1 |
| Tupaia belangeri | Tree_shrew | tupBel1 |
| Vicugna pacos | Alpaca | vicPac2 |
| Xenopus tropicalis | Frog | xenTro9 |