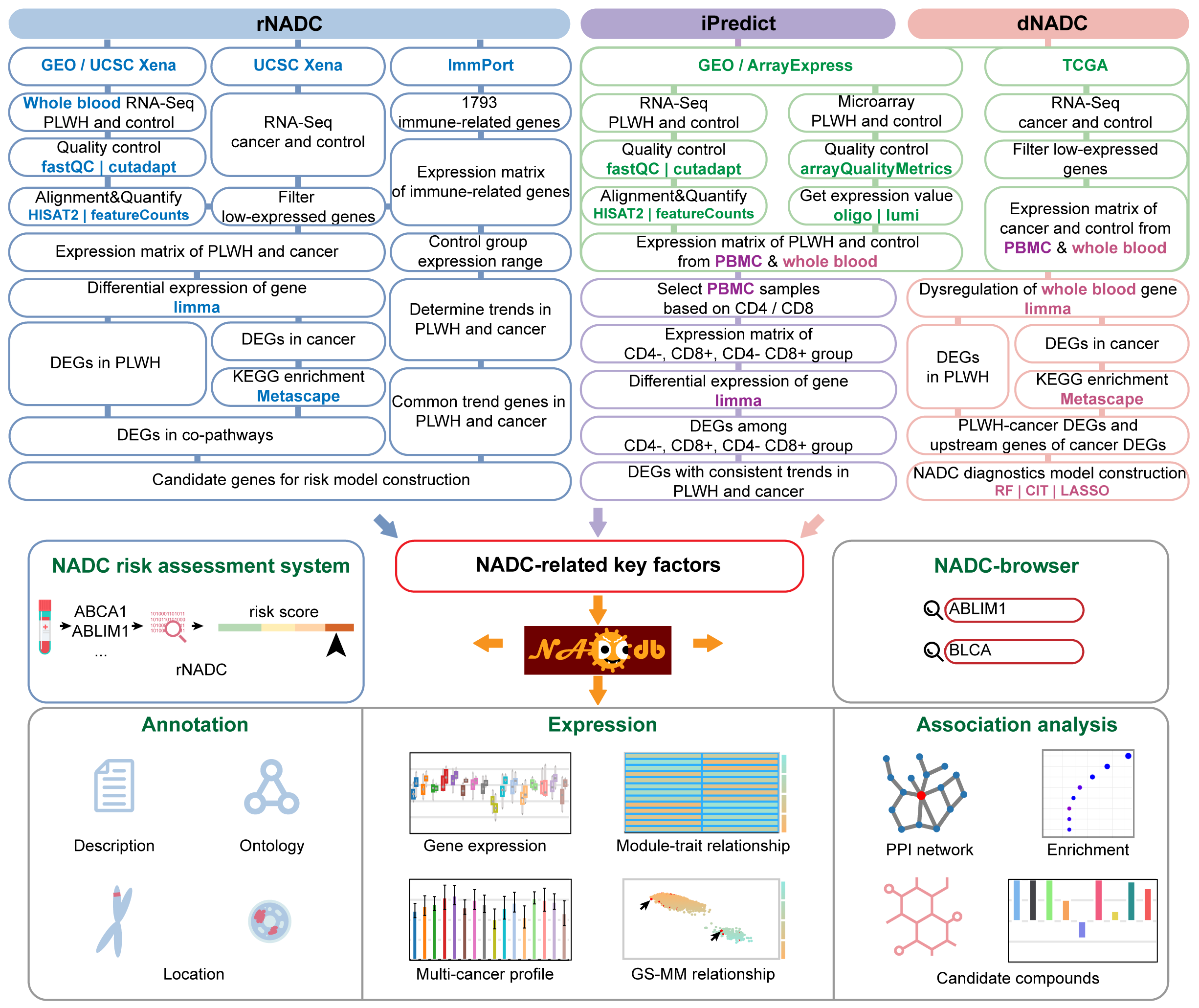
Welcome to NADCdb
NADCdb includes three core models namely "dNADC", "rNADC" and "iPredict" respectively. "rNADC" and its derivative tool was the first to utilize genes, that within the realms of immune suppression, chronic inflammation and oncogenic pathways, with abnormal expression trends as candidates, employing bidirectional stepwise regression and logistic regression to assess the risk of PLWH developing 21 NADCs. "dNADC" integrated patients' dysregulated genes and their regulatory networks, using Random Forest (RF) and Conditional Inference Trees (CIT) to identify key drivers influencing NADC progression with an accuracy exceeding 75%. "iPredict" is designed to highlight the primary impact of HIV on the immune system and identified 1,905 key immunobiomarkers for 16 NADCs based on distinct three immune statuses (CD4-, CD8+, CD4-CD8+) of patients. Importantly, the multi-dimensional analysis of the key factors was performed, including depth functional annotations, phenotype correlations, protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, TF-miRNA-target regulatory networks and CMap drug prediction, to deeply dissect their pathogenic mechanisms in regulating NADCs. Additionally, NADCdb provided multiple user-friendly webpages including "Cancer" and "Gene" for queries of interest and instructions. In summary, NADCdb aims to provide new insights and impetus for the mechanisms and treatment of NADC.
dNADC
Diagnosis Model
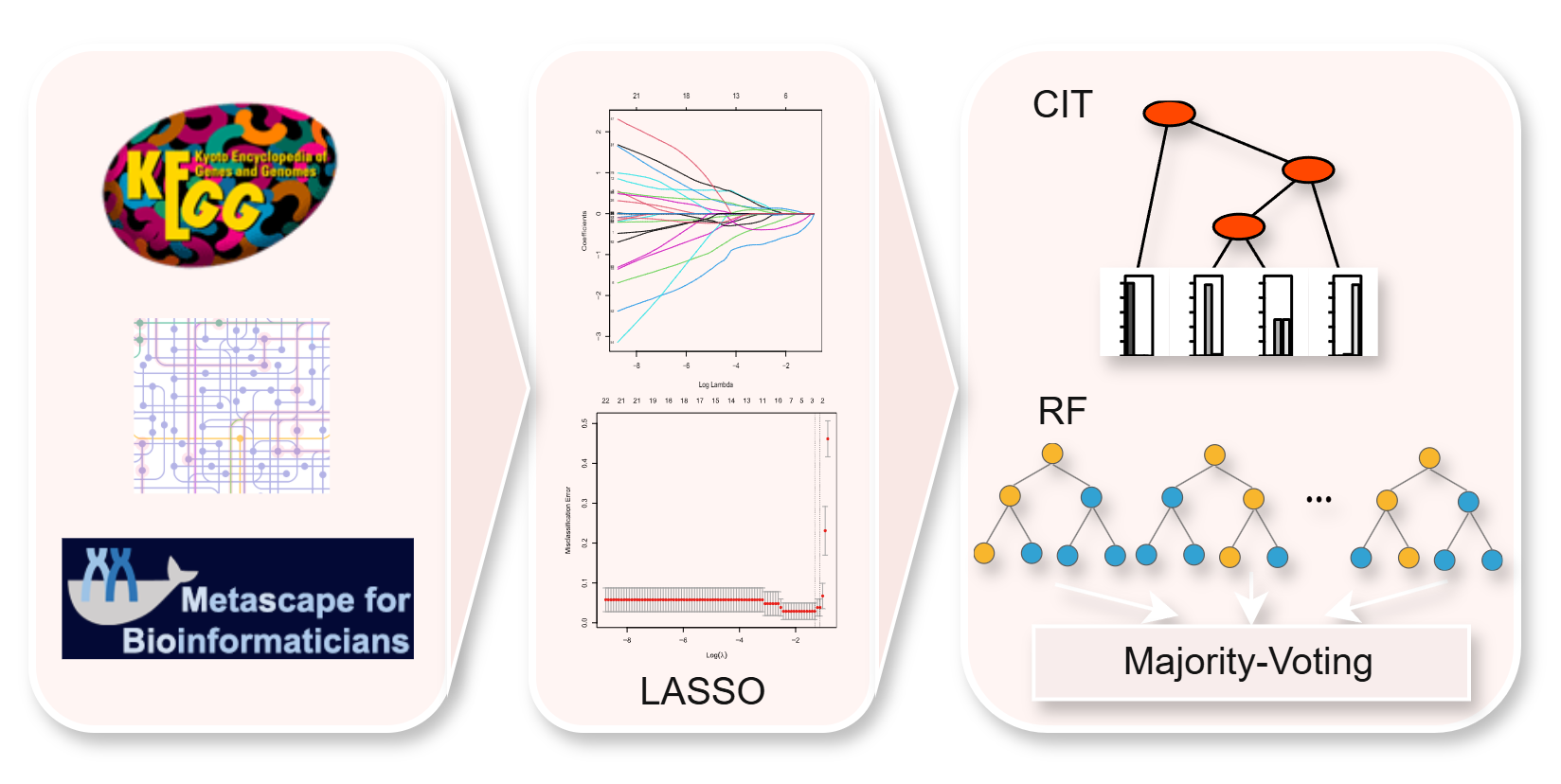
A diagnostic model for NADC developed by RF and CIT that based differential expressed genes (DEGs) in both PLWH and cancer patients, alongside the upstream regulatory factors within the HIV DEGs.
rNADC
Risk Assessment Model
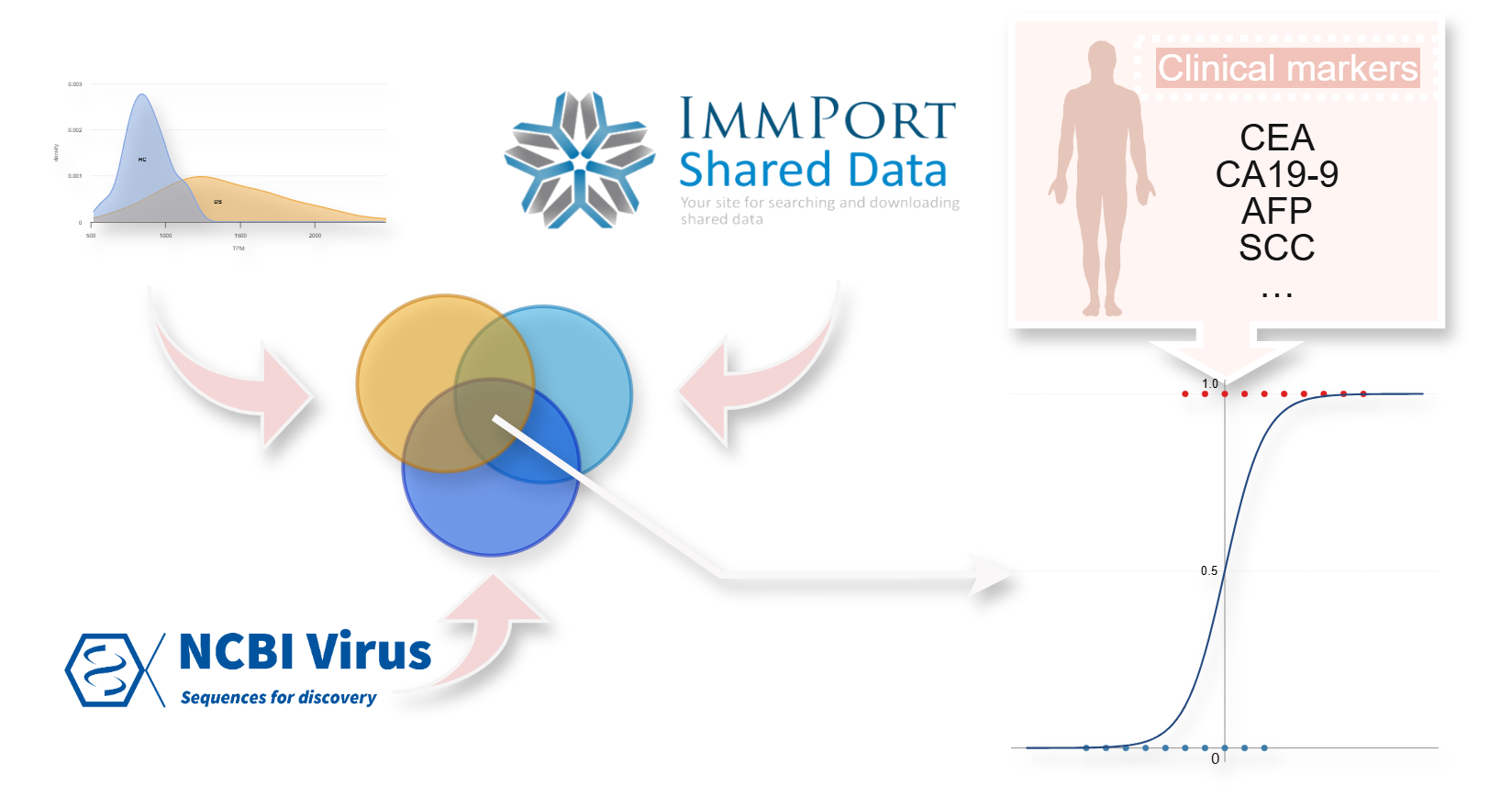
A risk assessment model to assess the risk of developing NADC by integrating immune and inflammatory indicators, viral interaction factors, and clinical biomarkers.
iPredict
Immunobiomarker Prediction
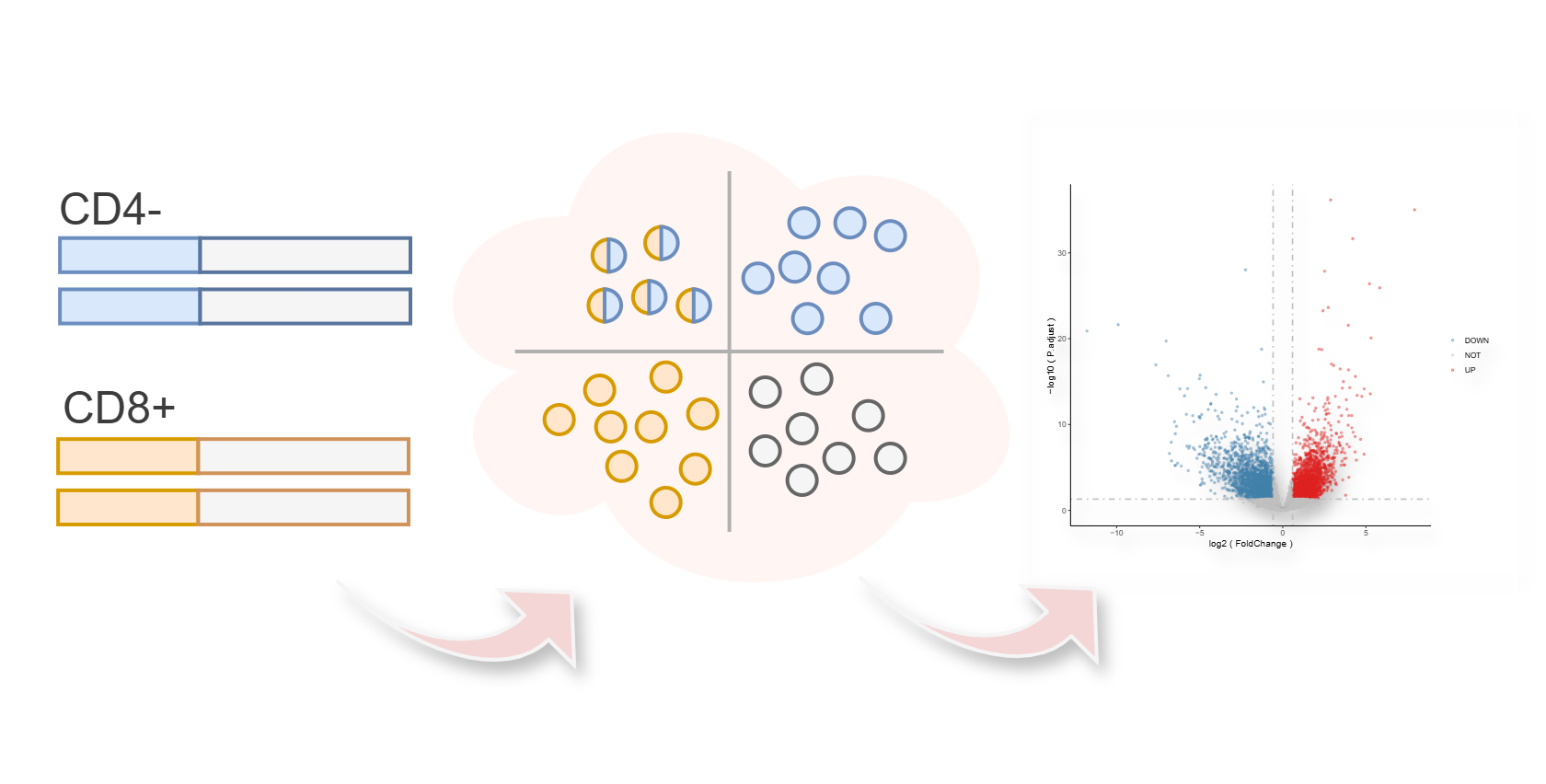
Predicted immunobiomarkers of NADC, which were consistent with immune characteristics following HIV infection, including "CD4-" (decreased CD4), "CD8+" (increased CD8) and "CD4-CD8+" (decreased CD4 accompanied by increased CD8).
Regulation
TF/miRNA-target regulatory pairs
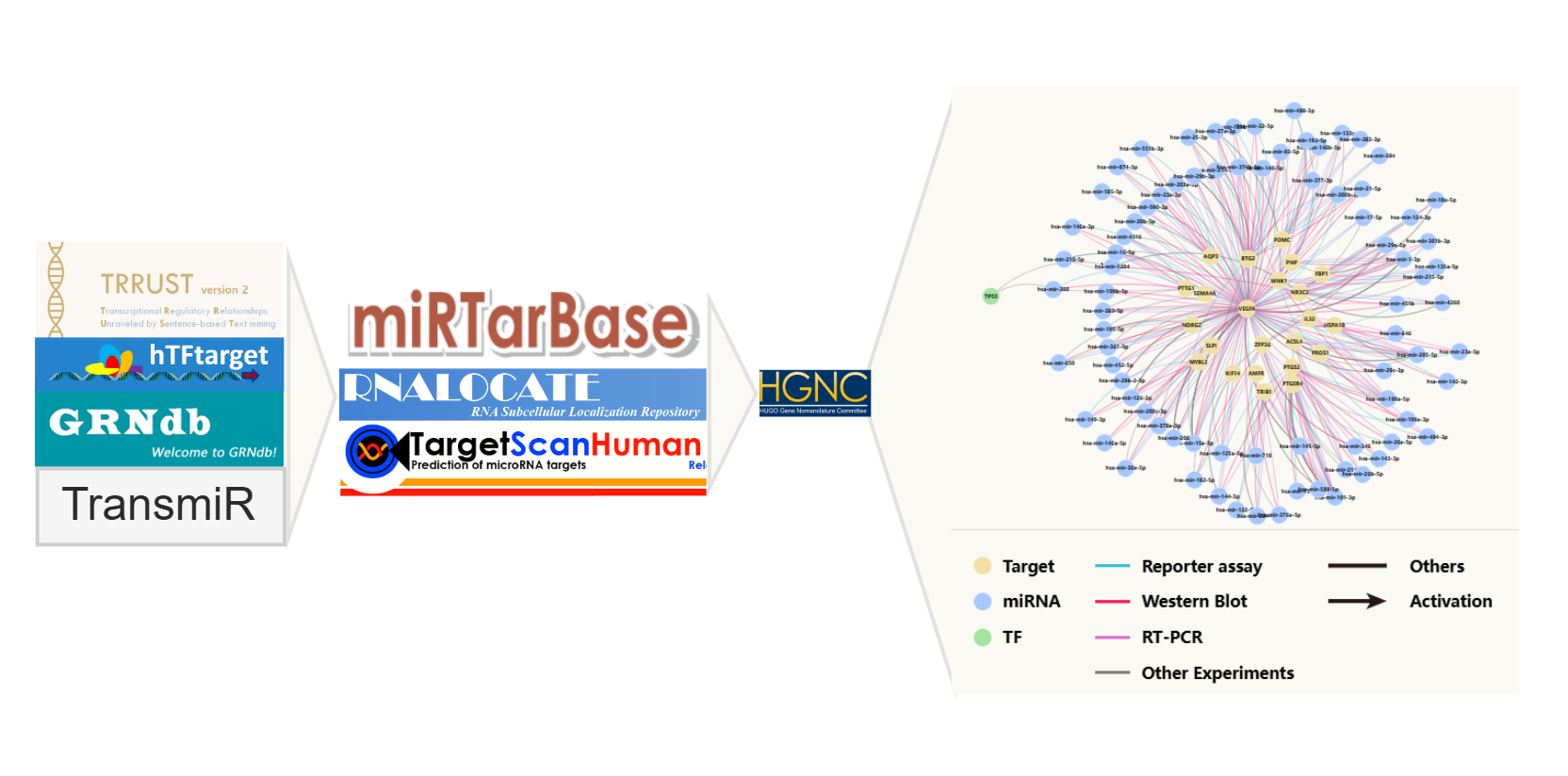
This module presents the complex regulatory networks involving NADC key factors, microRNAs (miRNAs) and transcription factors (TFs).
Cancer
Search of Cancer Case
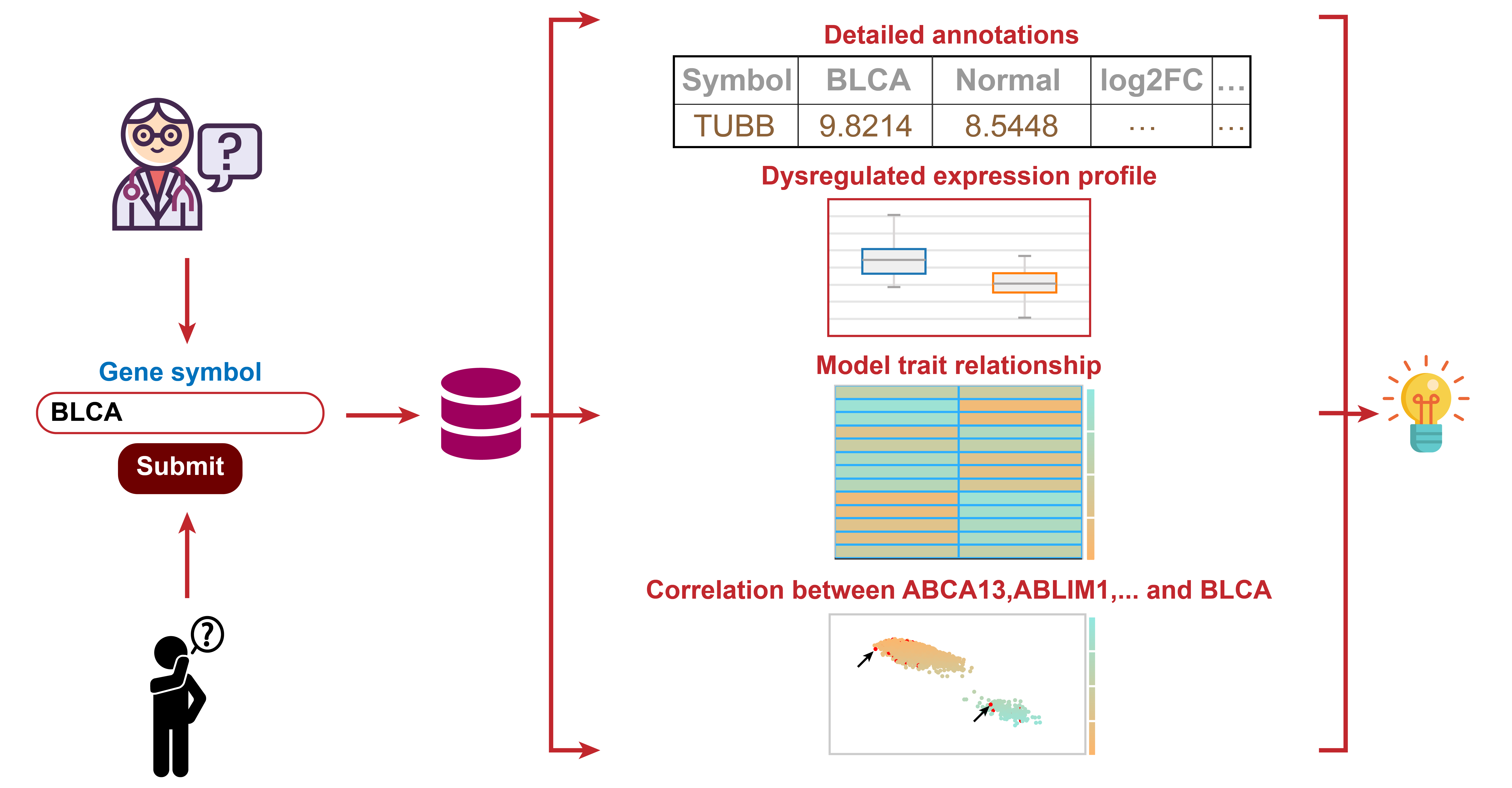
Discover potential biomarkers that may influence the development of 23 NADC types in PLWH.
Gene
Search of Gene Case
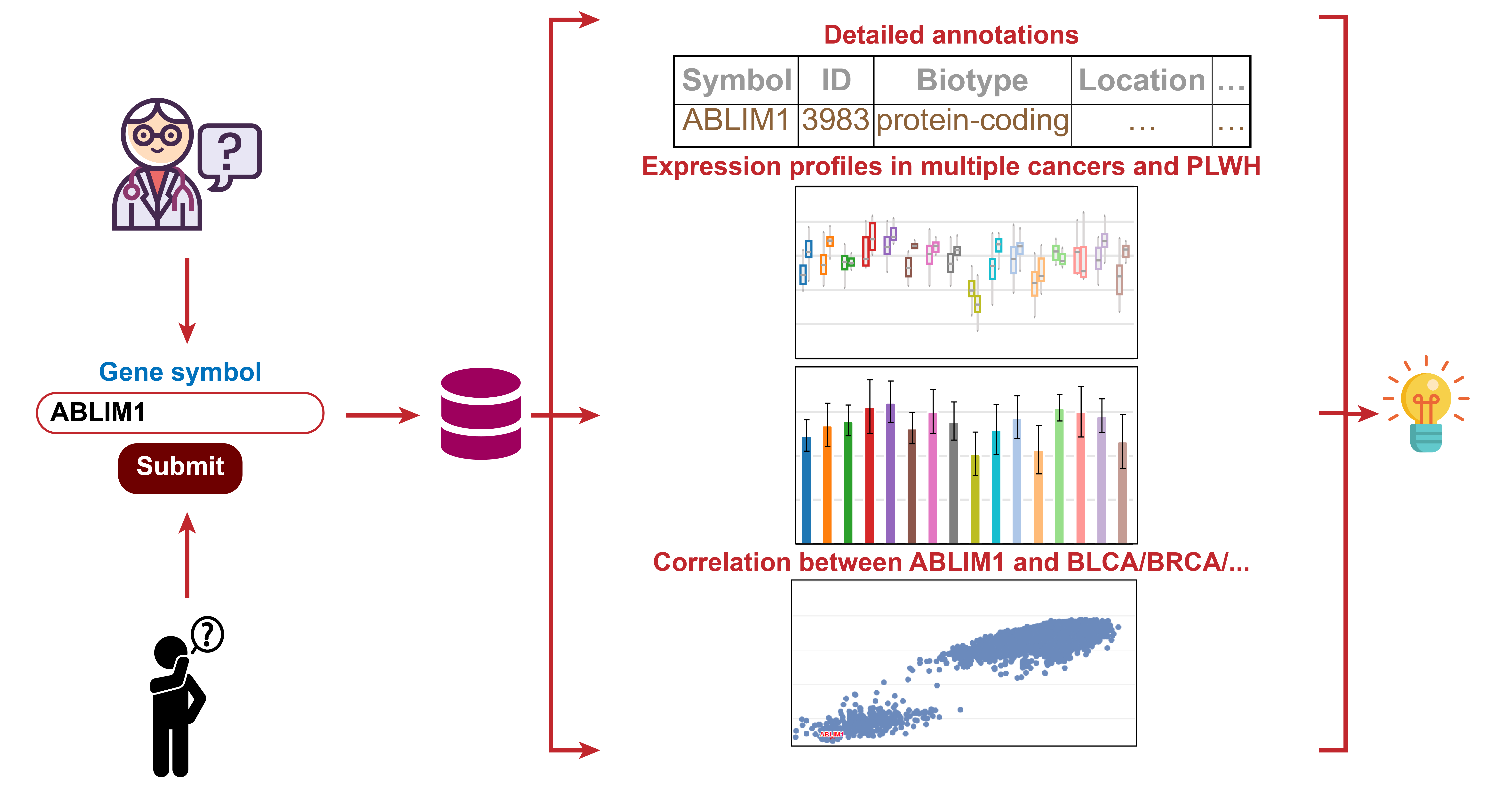
Decipher potential biological functions of key factors of interest that may influence the occurrence and development of NADC.